![]()
window.open( )
Creates a new secondary browser window and loads the referenced resource.
Syntax
WindowObjectReference = window.open(strUrl,
strWindowName [, strWindowFeatures]);
Return value and parameters
- WindowObjectReference
- This is the reference pointing to the newly created browser window. This reference is the return value of the open() method; such reference will exist only if the window.open() instruction succeeded. A global variable is best used to store such reference. This window reference can be useful and is needed to access properties and methods of the new browser window.
- strUrl
- This is the string of the referenced resource that will be loaded in the new window. strUrl can be an HTML document on the web, it can be an image file or any type of file which is supported by the browser.
- strWindowName
- This is the string that just names the new window. Such string can be used to be the target of links and forms when the target attribute of an <a> element or of a <form> is specified. This string parameter should not contain any blank space. strWindowName does not specify the title of the new window.
- strWindowFeatures
- Optional parameter. This parameter is the string which lists the requested window features (window functionalities and toolbars) of the new browser window. This string parameter must not contain any blank space. Each requested window feature must be separated by a comma inside the character string.
Description
The open method creates a new secondary browser window, similar to choosing New, then Navigator Window from the File menu. The strUrl parameter specifies the URL to be fetched and loaded in the new window. If strUrl is an empty string, then a new blank, empty window is created with all the default toolbars of the main window.
<script type="text/javascript">
var WindowObjectReference; /* Declaring a global variable
which will store a reference to the new window to be created */
function openRequestedPopup()
{
WindowObjectReference = window.open("http://www.cnn.com/", "CNN_WindowName",
"menubar=yes,location=yes,resizable=yes,scrollbars=yes,status=yes");
}
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var WindowObjectReference; // global variable
function openRequestedPopup()
{
WindowObjectReference = window.open("http://www.domainname.ext/path/ImageFilename.png",
"DescriptiveWindowName", "resizable=yes,scrollbars=yes,status=yes");
}
</script>
You can use the open method on an existing window, and if you pass the empty string for the URL, then you will get a reference to the existing window, but not load anything into it. You can then, for example, look for properties of that window or access its methods, assuming your code stores accordingly that returned window object reference and assuming that your main versus secondary window relationship complies with Same origin policy security requirements.
strWindowFeatures is an optional string containing a comma-separated list of requested features of the new window. After a window is open, you can not use JavaScript to change the window functionalities and the window toolbars.
If strWindowName does not specify an existing window and if you do not supply the strWindowFeatures parameter (or if the strWindowFeatures parameter is an empty string), then the new secondary window will render the default toolbars of the main window. In such case, under the Windows platform, the width and height dimensions of the new window are the same as the dimensions of the most recently rendered window and its left and top coordinate positions are 22 pixels off from where the most recently rendered window was. The purpose of such offset is to help users to notice new windows opening. If the most recently used window was maximized, then there is no 22 pixels offset: the new, secondary window will be maximized as well.
If you define the strWindowFeatures parameter, then the features that are not listed, requested in the string will be disabled or removed (except titlebar and close which are by default yes).
Tip: If you use the strWindowFeatures parameter, then list the features you want to include in the new window, that you want to be rendered and enabled; the others (except titlebar and close) will be removed, disabled.
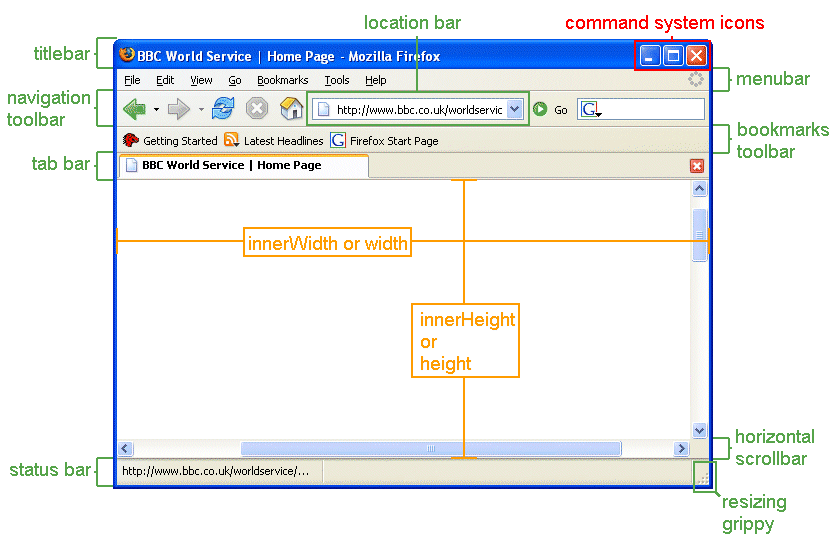
There are 3 groups of windowFeatures which can be specified:
Position and size features
Requested position and requested dimension values in the
strWindowFeatures list will not be honored and
will be corrected if any of such requested value does
not allow the entire browser window to be rendered within the work
area for applications of the user's operating system.
By default, no part of the new window can be initially positioned offscreen.
Bug 176320: Minimal innerWidth/innerHeight values for popup windows
Note on precedence
- left
- Specifies the distance the new window is placed from the left side of the work area for applications of the user's operating system to the leftmost border (resizing handle) of the browser window. The new window can not be initially positioned offscreen.
- top
- Specifies the distance the new window is placed from the top side of the work area for applications of the user's operating system to the topmost border (resizing handle) of the browser window. The new window can not be initially positioned offscreen.
- height
- Specifies the height of the content area, viewing area of the new secondary window in pixels. The height value includes the height of the horizontal scrollbar if present. The minimum required value is 100.
- width
- Specifies the width of the content area, viewing area of the new secondary window in pixels. The width value includes the width of the vertical scrollbar if present. The width value does not include the sidebar if it is expanded. The minimum required value is 100.
- screenX
- Deprecated. Same as left.
- screenY
- Deprecated. Same as top.
- outerHeight
Specifies the height of the whole browser window in pixels. This outerHeight value includes any/all present toolbar, window horizontal scrollbar (if present) and top and bottom window resizing borders. Minimal required value is 100.
Note: since titlebar is always rendered, then requesting outerHeight=100 will make the innerHeight of the browser window under the minimal 100 pixels.
- outerWidth
- Specifies the width of the whole browser window in pixels. This outerWidth value includes the window vertical scrollbar (if present) and left and right window resizing borders.
- innerHeight
- Same as height.
- innerWidth
- Same as width.
- fullscreen
- Do not use. Not implemented. There are no plan to implement this feature either.
Toolbar and chrome features
- location
If this feature is set to yes, then the new secondary window will render the Location bar.
Mozilla and Firefox users can force all windows to have a location bar by setting
dom.disable_window_open_feature.location
to true in about:config or in their user.js file.- menubar
If this feature is set to yes, then the new secondary window will render the menubar.
Mozilla and Firefox users can force all windows to have a menubar by setting
dom.disable_window_open_feature.menubar
to true in about:config or in their user.js file.- directories
If this feature is set to yes, then the new secondary window will render the Bookmarks Toolbar in Firefox and it will render the Personal Toolbar in other Mozilla-based browsers. In addition to the Personal Toolbar, Mozilla browser will render the Site Navigation Bar if such toolbar is visible, present in the parent window.
Mozilla and Firefox users can force new windows to always render the Personal Toolbar/Bookmarks toolbar by setting
dom.disable_window_open_feature.directories
to true in about:config or in their user.js file.- toolbar
If this feature is set to yes, then the new secondary window will render the Navigation Toolbar (Back, Forward, Reload, Stop buttons). In addition to the Navigation Toolbar, Mozilla-based browsers will render the Tab Bar if it is visible, present in the parent window.
Mozilla and Firefox users can force new windows to always render the Navigation Toolbar by setting
dom.disable_window_open_feature.toolbar
to true in about:config or in their user.js file.- status
- If this feature is set to yes, then the new secondary window will have a status bar. Users can force the rendering of status bar. The default setting is to force the presence of the status bar.
- personalbar
- Same as directories.
- titlebar
- By default, all new secondary windows always have a titlebar. If set to no and if enhanced privileged security access is granted by the user, then it would remove the titlebar from new secondary windows.
Window functionality features
- resizable
If this feature is set to yes, then it will make the new secondary window resizable.
Note: Mozilla-based browsers since version 1.4 will have a window resizing grippy at the right end of the status bar; this is to assure users that they can resize a browser window even when the web author explicitly or implicitly requested to make such secondary window non-resizable. In such case, the maximize/restore down system command icon in the titlebar will be disabled and window resizing borders will be unresponsive but the window will still be resizable via that window resizing grippy in the status bar.
Tip: For accessibility reasons, it is strongly recommended to always set this feature to yes.
Mozilla and Firefox users can force all windows to be easily resizable by setting
dom.disable_window_open_feature.resizable
to true in about:config or in their user.js file.- scrollbars
If this feature is set to yes, then the new secondary window will render scrollbar(s) if needed, only if document content box overflows window dimensions.
Tip: For accessibility reasons, it is strongly recommended to always set this feature to yes.
Users can force all windows to render scrollbars when needed, when a document content overflow occurs by setting
dom.disable_window_open_feature.scrollbars
to true in about:config or in their user.js file.- dependent
If set to yes, the new window is said to be dependent of its parent window. A dependent window closes when its parent window closes. A dependent window is minimized on the Windows task bar only when its parent window is minimized. On Windows platforms, a dependent window does not show on the task bar. A dependent window will also stay in front of the parent window.
- modal
If set to yes, the new window is said to be modal. The modal feature makes the new, secondary window stay on top/in front of its opener. Modal windows do not appear on the Windows task bar and can not be minimized on the Windows task bar. Another unrelated browser window may still be placed above the modal window.
The exact behavior of modal windows depends on the platform and on the Mozilla release version.
- dialog
- If set to yes, the new window is said to be a dialog window. Dialog windows are windows which have no minimize system command icon nor maximize/restore down system command icon on the titlebar. They are said to be dialog because their normal, usual purpose is to only notify info and to be dismissed, closed.
- minimizable
- This setting can only apply to dialog windows. If minimizable is set to yes, then the new dialog window will render a minimize system command icon and it will be minimizable.
- alwaysRaised
If set to yes, the new window to be created will float on top of, in front of any other browser windows, whether it is active or not. This feature requires enhanced privileged security access granted by the user.
At the time of writing this file, alwaysRaised feature is not supported when used in content scripts due to bug 274088; it works in chrome scripts though.
- alwaysLowered
If set to yes, the new created window will float below, under its own parent when the parent window is not minimized. alwaysLowered windows are often referred as pop-under windows. This feature requires enhanced privileged security access granted by the user.
At the time of writing this file, alwaysLowered feature is not supported when used in content scripts due to bug 274088.
- z-lock
- Same as alwaysLowered.
- close
- When set to no, this feature removes the system command
icons and system command menu. This feature requires both
enhanced privileged abilities granted by the user and the
feature
dialog=yes.close=nowill overrideminimizable=yes.
The position and size feature elements require a number to be set. The toolbars and window functionalities can be set with a yes or no; you can use 1 instead of yes and 0 instead of no. The toolbar and functionality feature elements also accept the shorthand form: you can turn a feature on by simply listing the feature name in the strWindowFeatures string.
<script type="text/javascript">
var WindowObjectReference; // global variable
function openRequestedPopup()
{
WindowObjectReference = window.open("http://www.domainname.ext/path/ImageFilename.png",
"DescriptiveWindowName",
"width=420,height=230,resizable,scrollbars=yes,status=1");
}
</script>
In this example, the window will be resizable, it will render scrollbar(s) if needed, if the content overflows window dimensions and it will render the status bar. It will not render the menubar nor the location bar.
FAQ
- How to bring back the window if
minimized or if the window is behind another window?
First check for the existence of the window object reference of such window and if it exists and if it has not been closed, then use focus() method. - How do I force a maximized window?
You can not. Mozilla browsers try to make the opening of new secondary windows noticed by users and noticeable by users to avoid confusion, to avoid disorienting users. - How do I turn off window resizability
or remove toolbars?
You can not by force. Mozilla users can have absolute control over window functionalities (resizability and scrollability) and toolbars presence by editing user preferences in about:config or via advanced prefs. We recommend to always set the resizability and scrollbars presence (if needed) to yes to insure accessibility to content and usability of windows. - How do I open a referenced resource
of a link into a new tab? or in a specific tab?
Currently, you can not. Only the user can set his advanced preferences to do that. - How do I know if a window has
opened, is still opened?
You can test for the existence of the window object reference which is the returned value in case of success of the window.open() call and then verify that WindowObjectReference.closed return value is false but this is not a reliable way to detect an active popup blocking software. - I can not access
the properties of the new secondary window. I always get a message in
the javascript console saying "Error: uncaught exception: Permission denied
to get property <property_name or method_name>". Why is that?
It is because of the cross-domain script security restriction (also referred as the "Same Origin Policy"). A script loaded in a window (or frame) from a distinct origin (domain name) cannot get nor set properties of another window (or frame) or the properties of any of its HTML objects coming from another distinct origin (domain name). Before executing a script, the browser in the main window verifies that the secondary window has the same domain name.
More reading on cross-domain script security restriction: The Same Origin Policy
Glossary
- Opener window, parent window, main window, first window
- terms often used to describe or to identify the same window. It is the window from which a new window will be created. It is the window on which the user clicked a link which lead to the creation of another, new window.
- Sub-window, child window, secondary window, second window
- terms often used to describe or to identify the same window. It is the new window which was created.
- Unrequested popup windows
- script-initiated windows opening automatically without the user's consent.
Specification
DOM Level 0. Not part of any W3C specification or technical recommendation.
Notes
Note on precedence
In cases where left and screenX (and/or top and screenY) have conflicting values, then left and top have precedence over screenX and screenY respectively. If left and screenX (and/or top and screenY) are defined in the strWindowFeatures list, then left (and/or top) will be honored and rendered.
WindowObjectReference = window.open("http://news.bbc.co.uk/",
"BBCNewsWindowName", "left=100,screenX=200,resizable,scrollbars,status");
In this example, the new window will be positioned at 100 pixels from the left side of the work area for applications of the user's operating system, not at 200 pixels.
If left is set but top has no value and screenY has a value, then left and screenY will be the coordinate positioning values of the secondary window.
outerWidth has precedence over width and width has precedence over innerWidth.
outerHeight has precedence over height and height has precedence over innerHeight.
WindowObjectReference = window.open("http://www.wwf.org/",
"WildlifeOrgWindowName",
"outerWidth=600,width=500,innerWidth=400,resizable,scrollbars,status");
In this example, Mozilla-based browsers will create a new window with an outerWidth of 600 pixels wide and will ignore the request of a width of 500 pixels and will also ignore the request of an innerWidth of 400 pixels.
Report errors or corrections
or relevant feedback to this file (bug 195867);
web design questions will be ignored.